Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), propelled by innovative tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, and IBM’s Watson X, has made significant inroads into everyday work, leaving virtually no industry untouched. With compelling and challenging use cases in banking and capital markets, healthcare, accounting, customer service, and much more, these tools, and those like them, transform the concept of chatbots and AI data platforms and, in turn, the very nature of corporate performance.
Today, business leaders are grappling with how to approach employee productivity, gain operational insights, and unleash creative potential now that GenAI has redefined organizational possibilities.
More urgently, they’re seeking to grasp what truly is and isn’t GenAI, what it’s capable of, and what they should keep top of mind in the months ahead.
What Really Is GenAI?
GenAI refers to artificial intelligence systems that have the ability to generate new content, such as text, code, images, audio, and video. Unlike traditional AI, which is focused on analysis and classification, GenAI takes a creative approach. It learns about connections between large volumes of data, building an understanding that allows it to produce original, realistic artifacts within certain guidelines.
To put it into perspective, imagine a tool that can swiftly summarize complex legal documents, sift through vast datasets for initial research, and propose creative and unconventional solutions to intricate problems – all within seconds. GenAI is engineered to perform human-like tasks while delivering exceptional speed and precision.
While GenAI is often associated with content creation, it also seamlessly integrates into a diverse spectrum of business applications. It proves its worth in fields as varied as automating data analysis, optimizing decision-making processes, enhancing customer experiences, and pushing the boundaries of creativity.
GenAI Myths and Misconceptions, Dispelled
GenAI represents a leap forward from both traditional rule-based AI as well as standard machine learning (ML), both of which are limited by their dependence on human-crafted logic and training data/inputs. GenAI models take in vastly more data from diverse sources, allowing for more flexible, generalizable learning.
Unlike earlier attempts at AI, modern generative systems can contextualize information and handle complex or novel prompts. With fine-tuning innovations like reinforcement learning, they continue to improve independently in an iterative process. However, GenAI does have limits in reasoning, intentionality, and judgment compared to human intelligence.
Below are common points of distinction to consider about GenAI:
- GenAI is intelligent or sentient: GenAI is not intelligent in the same way that humans are. GenAI models can learn to generate new content based on patterns they have learned from training data, but they do not have the ability to understand the context, emotions, and nuances that humans possess.
- GenAI is too risky for businesses to integrate right now: In the year or so since ChatGPT’s release, an entire GenAI industry has developed, with organizations of every size now using the technology in the normal course of business. It’s estimated that 56% of workers and 42% of all U.S. companies are already using GenAI. With the cost still relatively cheap, a greater risk may be waiting too long to experiment with and adopt GenAI where relevant. While there are risks, explored in a later section, they are not insurmountable.
- GenAI isn’t necessary: While it’s true that organizations can and have operated without GenAI for decades, the technology is creating a new frontier for corporate performance and workforce productivity. As is the case with any new technology, when adopted strategically and cost-effectively with supportive change management, GenAI can quickly prove its value and validate its necessity. Some of the ROI-positive metrics companies have reported so far have included time and cost savings, faster cycle times, and speed-to-research.
- GenAI will eliminate roles: Similar to previous technological advancements, job loss will be coupled with new job creation, as necessary skills shift toward other types of in-demand activities. GenAI can more immediately reduce the time it takes to accomplish certain manual tasks. Companies may opt to use that newfound employee bandwidth to achieve other higher-value or strategic tasks, or, depending on organizational and market factors, they could also simply cut hours or curtail future hiring in traditional areas of the business.
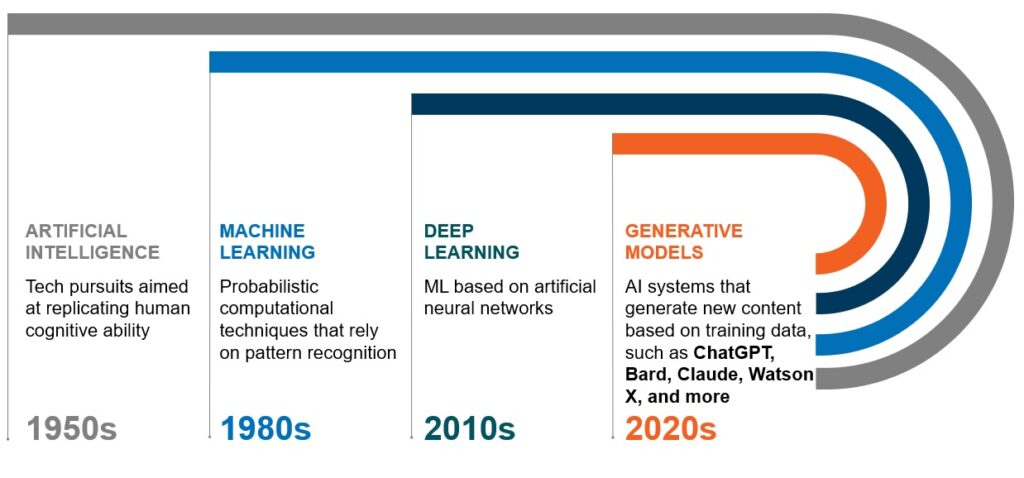
- How is GenAI different than chatbots or voice assistants? GenAI is the underlying technology enabling more advanced, conversational agents – not the agents themselves. These systems display generative abilities when creating fresh responses instead of matching pre-set queries and answers.
- How is GenAI different than traditional AI? Traditional AI is typically more efficient and interpretable than GenAI, but it’s also less creative and flexible. Traditional AI learns rules and patterns from data and then makes predictions or decisions, whereas GenAI learns patterns from data and generates new data.
- How is GenAI different than machine learning? Machine learning is a precursor to GenAI and is limited to human-crafted logic and data input/training. GenAI uses machine-learning algorithms to not just learn, classify, or predict data but to create entirely new forms of data and analysis.
- How is GenAI different than automation? Process automation tools are programmed to follow a fixed set of rules and conditions to automate specific tasks, like data entry or pricing retrieval. These tools often require a lot of training data and development time for narrow use cases. GenAI can also automate tasks but require less training and can handle more complex tasks that require creativity and original creation of content/data.
Unlocking New Opportunities While Navigating Risks
For businesses, GenAI unlocks new possibilities for saving time, costs, and human effort by assisting workers with some of their time-consuming tasks. It can serve up detailed market research reports, draft business proposals, generate product descriptions, code simple programs, and much more. As technology improves, so will its business applications.
However, as with any innovative technology, challenges exist. A key concern is that AI systems can hallucinate or generate false information if trained on low-quality, biased datasets. They may also favor common patterns over accuracy. Being aware of these limitations is important when deploying GenAI responsibly. Companies must have a thorough understanding of the associated risks and the necessary tools to mitigate them, including an adequate governance framework.
Explore expert Data Transformation & Analytics solutions that solve real-world problems
Accelerate strategic adoption of data, analytics, and artificial intelligence platforms within a scalable systems architecture for efficient reporting, cleaner insights, and greater change readiness.
Other relevant concerns include legal and ethical risks around copyright, data privacy, and the misuse of generative models for fraud or propaganda. As its capabilities grow, adequate regulation will be needed to protect against potential harm.
Several companies and global organizations have taken the lead to ensure AI development takes a human-centric approach. In 2019, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) published the “OECD AI Principles” aimed at providing guidelines for governments and other stakeholders to achieve trustworthy AI. In addition to this, Microsoft released its “Responsible AI standard” in 2022 as a response to filling the existing gap between legislation and the responsible usage of AI.
Looking Ahead with Cautious Optimism
Understanding GenAI’s realities, both positive and negative, will be key to leveraging its possibilities. Businesses can derive tremendous value from GenAI while also exercising diligence around ethics and security. With an informed, measured approach, this technology holds vast potential to augment human abilities and open new avenues of innovation.
When exploring how to integrate GenAI models into operations, a clear understanding of current offerings, capabilities, and limitations is imperative. The goal is to rigorously assess GenAI’s upsides and use cases while mitigating risk to the organization. Partnering with CrossCountry Consulting can offer invaluable guidance on how to identify GenAI’s integration and alignment potential with your current or future data strategy.
To get started on your GenAI journey, contact CrossCountry Consulting.
